DailyMed – SILDENAFIL tablet – Inergency
SUPER-1 (NCT00644605) -sildenafil tablets monotherapy [20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg three times a day]
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of sildenafil tablets (SUPER-1) was conducted in 277 patients with PAH (defined as a mean pulmonary artery pressure ≥25 mmHg at rest with a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure <15 mmHg). Patients were predominantly WHO Functional Classes II-III. Allowed background therapy included a combination of anticoagulants, digoxin, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, and oxygen. The use of prostacyclin analogues, endothelin receptor antagonists, and arginine supplementation were not permitted. Patients who had failed to respond to bosentan were also
excluded. Patients with left ventricular ejection fraction less than 45% or left ventricular shortening fraction less than 0.2 also were not studied.
Patients were randomized to receive placebo (n = 70) or sildenafil tablets 20 mg (n = 69), 40 mg (n = 67) or 80 mg (n = 71) three times a day for a period of 12 weeks. They had either primary pulmonary hypertension (PPH) (63%), PAH associated with CTD (30%), or PAH following surgical repair of left-to-right congenital heart lesions (7%). The study population consisted of 25% men and 75% women with a mean age of 49 years (range: 18 to 81 years) and baseline 6-minute walk distance between 100 and 450 meters (mean 343).
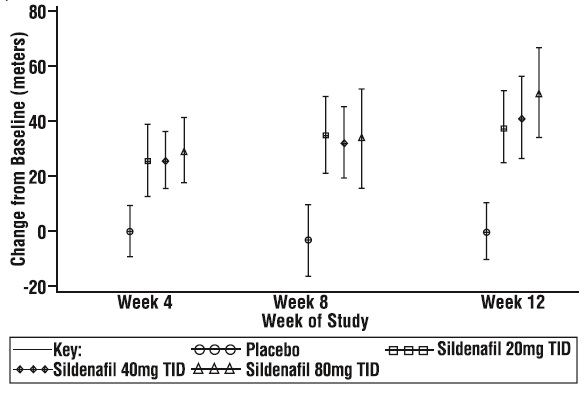
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline at Week 12 (at least 4 hours after the last dose) in the 6-minute walk distance. Placebo-corrected mean increases in walk distance of 45-50 meters were observed with all doses of sildenafil tablets. These increases were significantly different from placebo, but the sildenafil tablets dose groups were not different from each other (see Figure 3), indicating no additional clinical benefit from doses higher than 20 mg three times a day. The improvement in walk distance was apparent after 4 weeks of treatment and was maintained at Week 8 and Week 12.
Figure 3. Change from Baseline in 6-Minute Walk Distance (meters) at Weeks 4, 8, and 12 inSUPER-1: Mean (95% Confidence Interval)
Figure 4 displays subgroup efficacy analyses in SUPER-1 for the change from baseline in 6-Minute Walk Distance at Week 12 including baseline walk distance, disease etiology, functional class, gender, age, and hemodynamic parameters.
Figure 4. Placebo-Corrected Change From Baseline in 6-Minute Walk Distance (meters) at Week 12 by Study Subpopulation in SUPER-1: Mean (95% Confidence Interval)
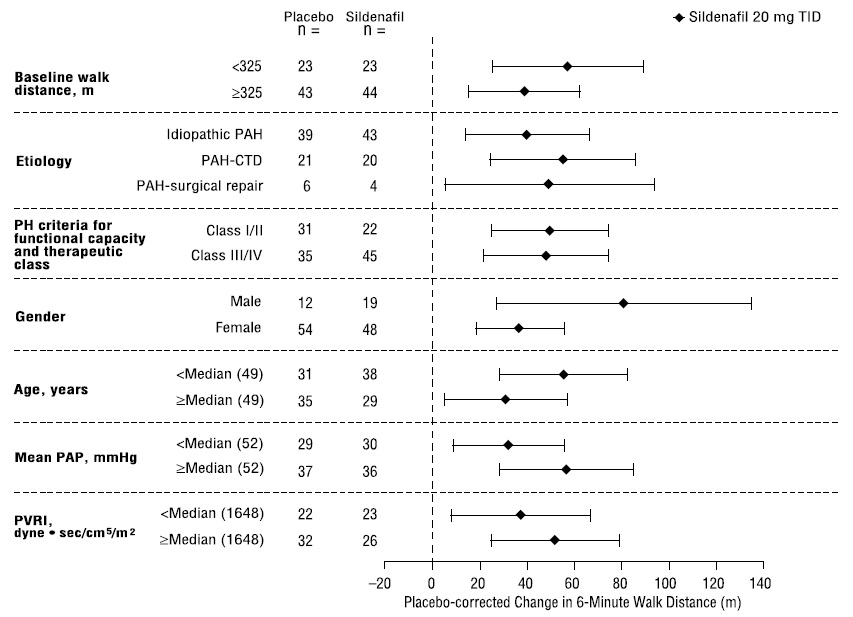
Key:PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension; CTD = connective tissue disease; PH = pulmonary hypertension; PAP = pulmonary arterial pressure; PVRI = pulmonary vascular resistance index; TID = three times daily.
SUPER-2 (NCT00159887) Long-term Treatment of PAH
In a long-term follow-up of patients who were treated with sildenafil (n=277), K-M estimates of survival at 1, 2, and 3 years were 94%, 88%, and 79%, respectively. These uncontrolled observations do not allow comparison with a group not given sildenafil and cannot be used to determine the long term-effect of sildenafil on mortality.
PACES-1 (NCT00159861) – Sildenafil tablets Co-administered with Epoprostenol
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study (PACES-1) was conducted in 267 patients with PAH who were taking stable doses of intravenous epoprostenol. Patients had to have a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) greater than or equal to 25 mmHg and a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) less than or equal to 15 mmHg at rest via right heart catheterization within 21 days before randomization, and a baseline 6-minute walk test distance greater than or equal to 100 meters and less than or equal to 450 meters (mean 349 meters). Patients were randomized to placebo or sildenafil tablets (in a fixed titration starting from 20 mg to 40 mg and then 80 mg, three times a day) and all patients continued intravenous epoprostenol therapy.
At baseline patients had PPH (80%) or PAH secondary to CTD (20%); WHO Functional Class I (1%), II (26%), III (67%), or IV (6%); and the mean age was 48 years, 80% were female, and 79% were Caucasian.
There was a statistically significant greater increase from baseline in 6-minute walk distance at Week 16 (primary endpoint) for the sildenafil tablets group compared with the placebo group. The mean change from baseline at Week 16 (last observation carried forward) was 30 meters for the sildenafil tablets group compared with 4 meters for the placebo group giving an adjusted treatment difference of 26 meters (95% CI: 10.8, 41.2) (p = 0.0009).
Patients on sildenafil tablets achieved a statistically significant reduction in mPAP compared to those on placebo. A mean placebo-corrected treatment effect of -3.9 mmHg was observed in favor of sildenafil tablets (95% CI: -5.7, -2.1) (p = 0.00003).
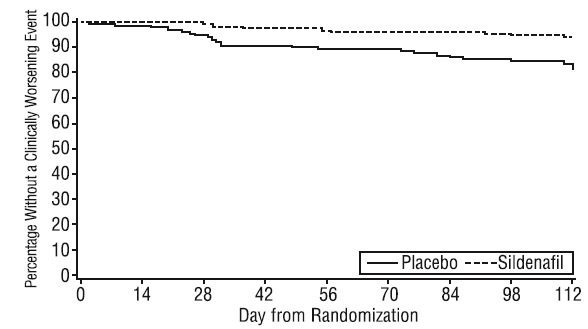
Time to clinical worsening of PAH was defined as the time from randomization to the first occurrence of a clinical worsening event (death, lung transplantation, initiation of bosentan therapy, or clinical deterioration requiring a change in epoprostenol therapy). Table 4 displays the number of patients with clinical worsening events in PACES-1. Kaplan-Meier estimates and a stratified log-rank test demonstrated that placebo-treated patients were 3 times more likely to experience a clinical worsening event than sildenafil tablets-treated patients and that sildenafil tablets -treated patients experienced a significant delay in time to clinical worsening versus placebo-treated patients (p = 0.0074). Kaplan-Meier plot of time to clinical worsening is presented in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Kaplan-Meier Plot of Time (in Days) to Clinical Worsening of PAH inPACES-1
Improvements in WHO Functional Class for PAH were also demonstrated in patients on sildenafil tablets compared to placebo. More than twice as several sildenafil tablets-treated patients (36%) as placebo-treated patients (14%) showed an improvement in at least one functional New York Heart Association (NYHA) class for PAH.
Study A1481243 (NCT00323297) – Sildenafil tablets Added to Bosentan Therapy – Lack of Effect on Exercise Capacity
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in 103 patients with PAH who were on bosentan therapy for a minimum of 3 months. The PAH patients included those with primary PAH and PAH associated with CTD. Patients were randomized to placebo or sildenafil (20 mg three times a day) in combination with bosentan (62.5 to 125 mg twice a day). The primary efficacy endpoint was the change from baseline at Week 12 in 6-minute walk distance (6MWD). The results indicate that there is no significant difference in mean change from baseline on 6MWD observed between sildenafil 20 mg plus bosentan and bosentan alone.
Pediatric use information is approved for Viatris Specialty LLC’s, REVATIO (sildenafil) tablets. However, due to Viatris Specialty LLC’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that information.