Ozone Pollution Likely to Increase Disease Burden in India
[ad_1]
By Tara Failey
Luke Conibear, Ph.D., co-authored the study, titled “Current and Future Disease Burden from Ambient Ozone Exposure in India,” with colleagues at the University of Leeds and Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
(Photo courtesy of Luke Conibear)
Ambient ozone may have a more detrimental impact on India’s disease burden than previously estimated, according to a recent study from the University of Leeds. The findings, published October 2018 in GeoHealth, also reveal that premature mortalities in India due to ambient ozone are likely to increase significantly by 2050 if emissions continue at current levels.
“Our goals were to understand the current and future disease burden from ambient ozone exposure in India, identify key contributing emission sources, and explore the impacts of future policy scenarios,” said study lead author Luke Conibear, Ph.D., a research fellow at the Institute for Climate and Atmospheric Science at the University of Leeds. To understand the disease burden, the team used a state-of-the-science model to simulate ozone in South Asia, which was evaluated against ozone ground measurements. They used an updated risk function from the American Cancer Society Cancer Prevention Study II to estimate health impacts.
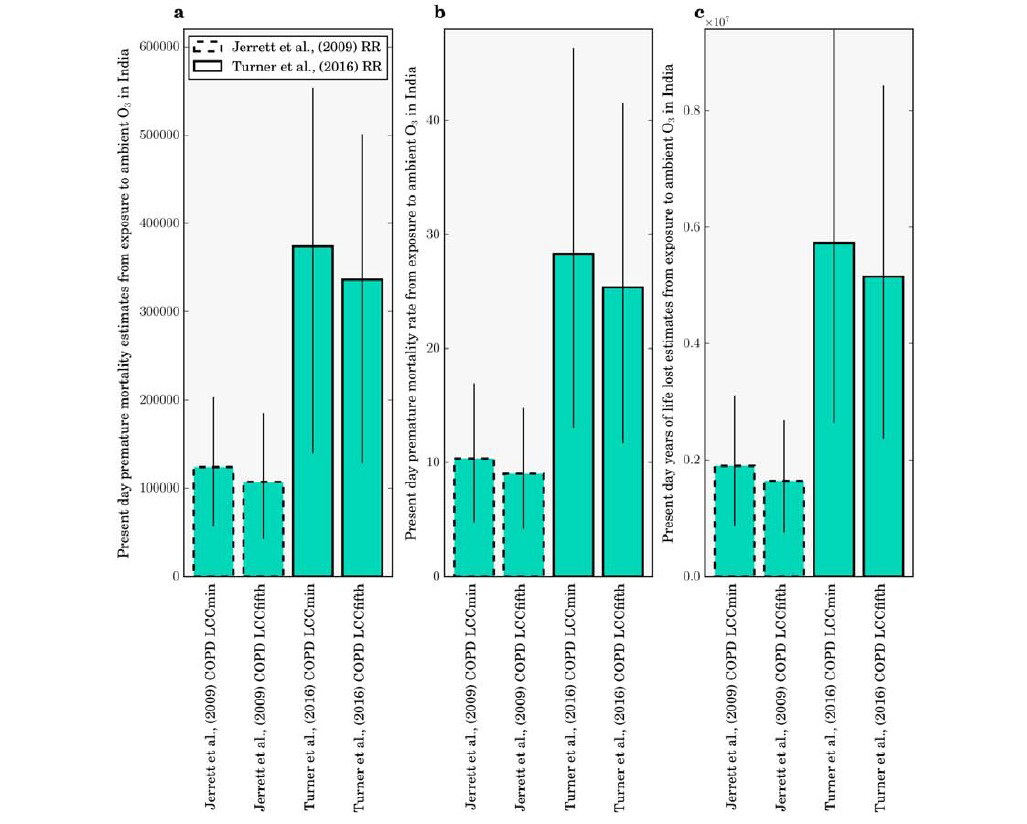
“Our findings show that an estimated 374,000 people die prematurely every year in India from exposure to ozone; this is 200 percent larger than previous estimates using an earlier old risk function,” said Conibear. With no change in emissions by 2050, Conibear and co-authors estimated 1,126,000 premature mortalities due to ozone each year. This would be an increase of 200 percent relative to the current day.
Ozone pollution near the Earth’s surface is created by the chemical reaction between sunlight, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. Ozone is one of the main ingredients of smog and a primary cause of poor air quality. It is linked to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. India contributes one-third of the global disease burden due to ozone exposure, according to the Global Burden of Disease 2017 study and data.
A Growing Problem in India
India is estimated to have some of the worst air pollution levels in the world. As the country has developed, air pollution levels have increased in part due to changing energy demand, urbanization, land use, and poor air quality policies. To date, most of the air pollution disease burden has been attributed to fine particulate matter particles, which can travel deep into the lungs and bloodstream, damaging the lungs and heart. However, according to Conibear, their team’s study highlights that the disease burden from ozone may worsen in the future and be similar in magnitude to that from fine particulate matter.
Conibear further explained that the disease burden due to air pollution will likely further increase due to the aging population and population growth. “The population of India is currently young, and as it ages and grows in the future, susceptibility to disease associated with air pollution will likely increase.”
To better understand how to mitigate the problem, the research team sought to learn more about the contribution of different emission sources to air pollution. “Despite the importance of air quality in India, it remains relatively understudied and knowledge of the sources and processes causing air pollution is limited,” said Conibear. Using high-resolution emissions, they found that the largest source of ozone-forming pollution came from land transport emissions (35 percent), followed by emissions for power generation (23 percent).
Cutting Emissions to Address Disease Burden
NIEHS workshop addresses pollution and human health

(Photo courtesy of Steve McCaw)
On Nov. 26, 2018, the NIEHS Office of the Director hosted three speakers for a workshop focused on addressing the health threats of pollution.
“This issue is particularly critical because pollution kills three times more people than AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis combined,” said John Balbus, M.D., NIEHS senior advisor for public health.
Learn more about the workshop in this recent Environmental Factor article.
“Our results suggest that there’s a need for large and rapid emission reductions, and that doing so can provide important public health benefits in a challenging environment,” said Conibear.
According to the paper authors, India’s existing and planned policies to reduce emissions, as assessed using the International Energy Agency’s (IEA’s) New Policy Scenario, would provide a minimal impact on the increasing disease burden. However, they argue that more ambitious emissions reductions, under the IEA’s Clean Air Scenario, could avert 30 percent, or 335,000, of the estimated annual premature mortalities in 2050, when compared to the scenario of no emission change.
“Despite population growth and aging increasing the attributable disease burden from ozone exposure, our study highlights that critical public health benefits are possible with stringent emission reductions,” said Conibear.
Citation: Conibear L, Butt EW, Knote C, Spracklen DV, Arnold SR. 2018. Current and future disease burden from ambient ozone exposure in India. Geohealth (2)334–355. doi:10.1029/2018GH000168. [Abstract]
[ad_2]


